1. An introduction to the physical property that your
group was investigating and how it is related to IMF´s.
The evaporation rate of a material is the rate at which it will vaporize,
this is, change from liquid to vapor, compared to the rate of vaporization of a
specific standard known material. The general reference material for
evaporation rates is n-butyl acetate (commonly
abbreviated BuAc).
Moreover, it is important to know that evaporation rates normally have an
inverse relationship to boiling points. The higher the boiling point, the lower
the rate of evaporation.
This physical property is clearly related to IMF’s. If the chemical we are
studying has weak intermolecular forces, it will need very little energy to
break the bonds and therefore the molecules would separate easily from each and
would vaporize quicker. This chemical would have a high evaporation rate as many
molecules would reach the gas phase.
However, if the substance had strong IMF’s it would require much more
energy in order for the molecules to separate, vaporize and reach the gas
phase, as the bonds would be very tight. Therefore, very few molecules would
evaporate and they would do it slower. The substance would have a low
evaporation rate.
In conclusion, strong IMF’S slow evaporation rates and weak IMF’s
accelerate evaporation rates.
2. A description of the 2 groups of chemicals
including; name, structure and types of IMF present.
Group 1 – Similar Molecular Weight: All the compounds in the following
table have very similar molecular masses.
Group 2 – Homologous Series: The compounds in this table have a
very similar structures and vary only by the number of CH2 units in the main
carbon chain.
3. A prediction (hypothesis) of the results you expect
with scientific explanations.
According to the theoretical background we
expect certain results. We expect a substance with stronger IMF’s to have a
lower evaporation rate, because it needs more energy in order to break its
molecular bonds and so, less molecules would be able to reach the gas phase and
they would do it slower. Some examples of these chemicals from Groups 1 and 2
are: Butanol, Propanoic acid, Propyl acetate and Butyl acetate, as they have
Hydrogen Bonding, which is the strongest type of IMF.
As to substances with weaker IMF’s (Van der
Waal’s and Dipole-Dipole forces), such as Diethyl Ether, Pentane, Methyl
acetate and Ethyl acetate, they should have higher evaporation rates as they
need less energy to break down bonds and more particles have more facility to
reach the gas phase.
Butyl Acetate
Deithyl Ether
Propyl Acetate
Ethyl Acetate
Methyl Acetate
Pentane
Butanol
Propanoic Acid
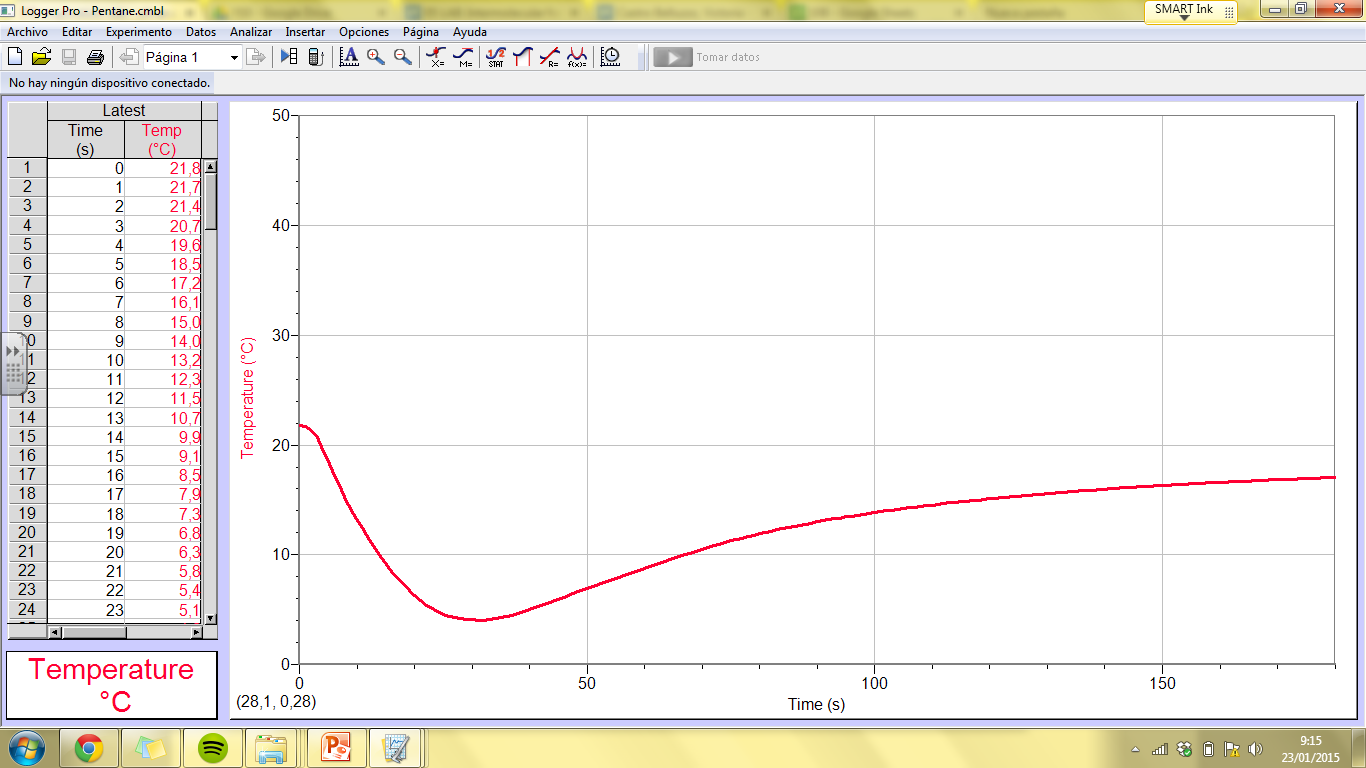
5. To what extent do your results match what you had expected
The results that
we have come up with match exactly what we were expecting. Compounds with
strong intermolecular forces evaporated very little or didn’t at all. We would say the evaporation rate of these was
minimal. However, the compounds with weaker intermolecular forces did evaporate
and consequently have a higher evaporation rate. We can see this perfectly in
the graphs. When the curvature is bigger, the higher
the evaporation rate is.
We can say we are
very satisfied with the data we recorded since it looks totally coherent.
6. An
evaluation explaining areas where error could have occurred and how you would
improve these areas in a future investigation.
So maybe the angle in which we put the stick inside the test tube wasn’t always the same and this could have altered the results since the machine might not have gotten enough data. A possible solution to this would be to leave the stick in the test tube somewhere without moving it and this way the machine would always be in the same position and therefore the information would have been gathered always the same way.
Another error in the method was that we didn’t measure the temperature of the test tube. If we don’t heat or cool the test tube to reach a certain temperature we don’t know if the temperatures in the different test tubes are the same. This is an essential fact when talking about evaporation rates as depending on temperature, which gives energy to the molecules inside chemicals, bonds in the substances will be more or less able to break down, which has a direct consequence on the vaporization of its particles. If temperature is lower, a chemical with strong bonds, such as hydrogen bonds, would have a very low evaporation rate. So, if we don’t have the same temperatures in each test tube, results won’t be reliable. A possible solution for this is simply measuring the temperature of each of the test tubes with a thermometer in order to have the same at each time. If needed we must heat or cool the test tube.
Apart from this, we could have improved our accuracy while doing the experiment. But this is our mistake and we wouldn’t have to change the method for this.
7. At least
2 references in APA format.
Pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov,.
(2015). PubChem. Retrieved 25 January 2015, from
BusinessDictionary.com,.
(2015). What is evaporation rate? definition and meaning. Retrieved 25 January
2015, from http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/evaporation-rate.html
Ilpi.com,.
(2015). The MSDS HyperGlossary: Evaporation Rate. Retrieved 25 January 2015,
from http://www.ilpi.com/msds/ref/evaporationrate.html
Socratic.org,.
(2015). How do intermolecular forces affect evaporation? | Socratic. Retrieved
25 January 2015, from http://socratic.org/questions/how-do-intermolecular-forces-affect-evaporation









Stick = thermometer!!!
ResponderEliminarThis is generally a well detailed report but really needs some kind of data related to the graph. I told you not to use the table from the logger pro as it was extremely long but you could have simply included somthing like the lowest temperature reached to support your conclusion. Also please give clear titles for graphs - Graph to show...
Asides from this point the report is very well structured and detailed.
7/8